What’s the difference between AWS Regions and AWS Availability Zones
By Dillon Smart · · · 0 Comments
AWS (Amazon Web Services) is built with scalability and high availability at its heart.
Not too long ago, I took the AWS Cloud Practitioner class and passed the AWS Cloud Essentials exam, with the hope of achieving the Cloud Practioner certification soon.
During the class, I noticed it was easy to get muddled between AWS Regions and Availability Zones when discussing cloud infrastructure on AWS.
AWS Regions and AWS Availability Zones are geographic locations but very different.
What is an AWS Region
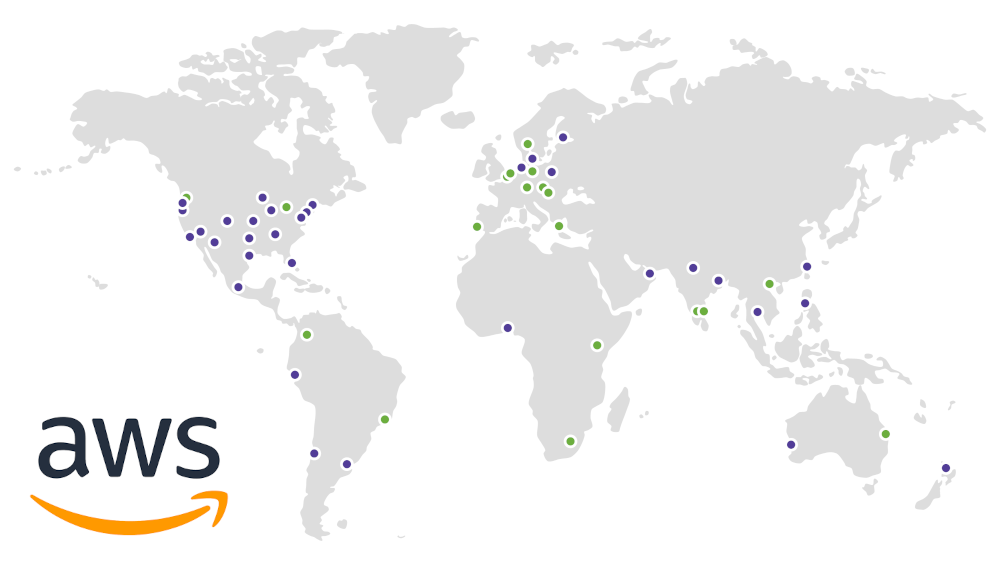
AWS cloud infrastructure is split between separate geographic areas, called Regions. As of January 2024, Amazon Web Services comprises 35 Regions, spanning the globe.
Each AWS Region is completely isolated from all other Regions, so when starting with AWS, the most important decision you need to make is picking the Region that suits your needs.
It’s important to know that not every AWS Region provides the same cloud services and services within a Region can not link with services outside of your chosen AWS Region. Pricing for services between Regions can also differ, and in many cases, this is the deciding factor when choosing your AWS Region.
Things to consider when choosing an AWS Region
There are several things to consider when choosing your AWS Region. Here is a list, in order, that Amazon recommended you consider when selecting your Region:
- Proximity to your customers
- Services available in your Region
- Cost of services within the Region
- Number of Availability Zones
What is an AWS Availability Zone
AWS Regions are made up of multiple Availability Zones (AZ). An AZ is a data center within a Region, which is geographically isolated from other Availability Zones within the Region. This is to ensure fault isolation between Availability Zones, such as natural disasters, network outages, or a thermal incident to name a few.
Each AWS Availability Zone is separated by at least 100km (60 miles). To ensure the high availability of your application, Amazon recommends deploying your application infrastructure across multiple Availability Zones within your Region.
Each AWS Region has at least 3 Availability Zones and each AZ has the same services available within the Region, so you don’t have to worry about a service your infrastructure relies on not being available in another AZ.
Conclusion
An AWS Region is a geographical area that comprises multiple Availability Zones. It’s important to choose the correct Region when planning out your cloud infrastructure, as not every AWS Service is available in all Regions.
0 Comment